Virtual machine and contract¶
Execution of transaction is an important function of blockchain nodes. It is the process to extract binary code of smart contract from the transaction and execute by Executo_. Consensus model takes transaction out of TxPool, seals into block and calls executor to execute the transaction in block. When the transaction is being executed, it will change the State of blockchain and become new block status for storage. Executor works like a black box, inputting smart contract code and outputting state change.
With the technological development, people start to concern about the performance and usability of executor. On one hand, they want faster execution speed of smart contract on blockchain to meet large scale of transactions; on the other hand, they want to use familiar and easy development language. So, some solutions are proposed to replace traditional EVM: JIT, WASM and JVM. However, traditional EVM is coupled in node code. The first step is to abstract the API of executor to adapt for realization of all kinds of virtual machines. That is why EVMC is designed.
EVMC (Ethereum Client-VM Connector API) is the API of executor abstracted by Ethereum to adapt to all kinds of executors. FISCO BCOS currently adopts smart contract language Solidity of Ethereum, and also, the abstraction of executor API.
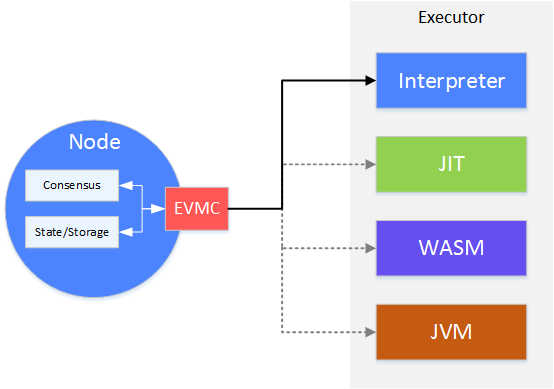
Consensus model will call EVMC on nodes and send sealed transaction to executor. The read/write of executor on status will be operated on the status data of nodes in return through call-back of EVMC.
Through the abstraction in EVMC level, FISCO BCOS can adapt to future executors with higher efficiency and usability. Currently, FISCO BCOS adopts executor abstracted through EVMC of traditional EVM—Interpreter. So, it supports smart contract based on Solidity. Other types of executors will be followed up in the future.